With these ten personal cybersecurity tips, we are aiming to help our readers become more cyber aware. We developed these security tips from our experience managing millions of security events for businesses and professionals worldwide.
The Top 10 Personal Cyber Security Tips
1. Keep Your Software Up to Date
As we saw from the stats above, ransomware attacks were a major attack vector of 2017 for both businesses and consumers. One of the most important cybersecurity tips to mitigate ransomware is patching outdated software, both operating systems, and applications. This helps remove critical vulnerabilities that hackers use to access your devices. Here are a few quick tips to get you started:
- Turn on automatic system updates for your device
- Make sure your desktop web browser uses automatic security updates
- Keep your web browser plugins like Flash, Java, etc. updated
Check out our blog on patch management best practices!
2. Use Anti-Virus Protection & Firewall
Anti-virus (AV) protection software has been the most prevalent solution to fight malicious attacks. AV software blocks malware and other malicious viruses from entering your device and compromising your data. Use anti-virus software from trusted vendors and only run one AV tool on your device.
Using a firewall is also important when defending your data against malicious attacks. A firewall helps screen out hackers, viruses, and other malicious activity that occurs over the Internet and determines what traffic is allowed to enter your device. Windows and Mac OS X comes with their respective firewalls, aptly named Windows Firewall and Mac Firewall. Your router should also have a firewall built in to prevent attacks on your network.
3. Use Strong Passwords & Use a Password Management Tool
You’ve probably heard that strong passwords are critical to online security. The truth is passwords are important in keeping hackers out of your data! According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s (NIST) 2017 new password policy framework, you should consider:
- Dropping the crazy, complex mixture of upper case letters, symbols, and numbers. Instead, opt for something more user-friendly but with at least eight characters and a maximum length of 64 characters.
- Don’t use the same password twice.
- The password should contain at least one lowercase letter, one uppercase letter, one number, and four symbols but not the following &%#@_.
- Choose something that is easy to remember and never leave a password hint out in the open or make it publicly available for hackers to see
- Reset your password when you forget it. But, change it once per year as a general refresh.
If you want to make it easier to manage your passwords, try using a password management tool or password account vault. LastPass FREE is a great tool for an individual. LastPass offers a FREE account and has a $2/month membership with some great advanced password features.
4. Use Two-Factor or Multi-Factor Authentication
Two-factor or multi-factor authentication is a service that adds additional layers of security to the standard password method of online identification. Without two-factor authentication, you would normally enter a username and password. But, with two-factor, you would be prompted to enter one additional authentication method such as a Personal Identification Code, another password or even fingerprint. With multi-factor authentication, you would be prompted to enter more than two additional authentication methods after entering your username and password.

According to NIST, an SMS delivery should not be used during two-factor authentication because malware can be used to attack mobile phone networks and can compromise data during the process.
5. Learn about Phishing Scams – be very suspicious of emails, phone calls, and flyers
In a phishing scheme attempt, the attacker poses as someone or something the sender is not to trick the recipient into divulging credentials, clicking a malicious link, or opening an attachment that infects the user’s system with malware, trojan, or zero-day vulnerability exploit. This often leads to a ransomware attack. In fact, 90% of ransomware attacks originate from phishing attempts.
A few important cybersecurity tips to remember about phishing schemes include:
- Bottom line – Don’t open an email from people you don’t know
- Know which links are safe and which are not – hover over a link to discover where it directs to
- Be suspicious of the emails sent to you in general – look and see where it came from and if there are grammatical errors
- Malicious links can come from friends who have been infected too. So, be extra careful!
6. Protect Your Sensitive Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
Personal Identifiable Information (PII) is any information that can be used by a cybercriminal to identify or locate an individual. PII includes information such as name, address, phone numbers, date of birth, Social Security Number, IP address, location details, or any other physical or digital identity data. Your credit card information should be protected by companies if they follow the PCI DSS standards.
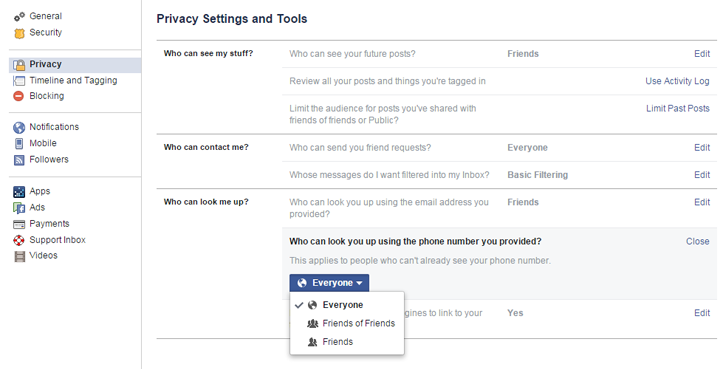
In the new “always-on” world of social media, you should be very cautious about the information you include online. It is recommended that you only show the very minimum about yourself on social media. Consider reviewing your privacy settings across all your social media accounts, particularly Facebook. Adding your home address, birth date, or any other PII information will dramatically increase your risk of a security breach. Hackers use this information to their advantage!
7. Use Your Mobile Devices Securely
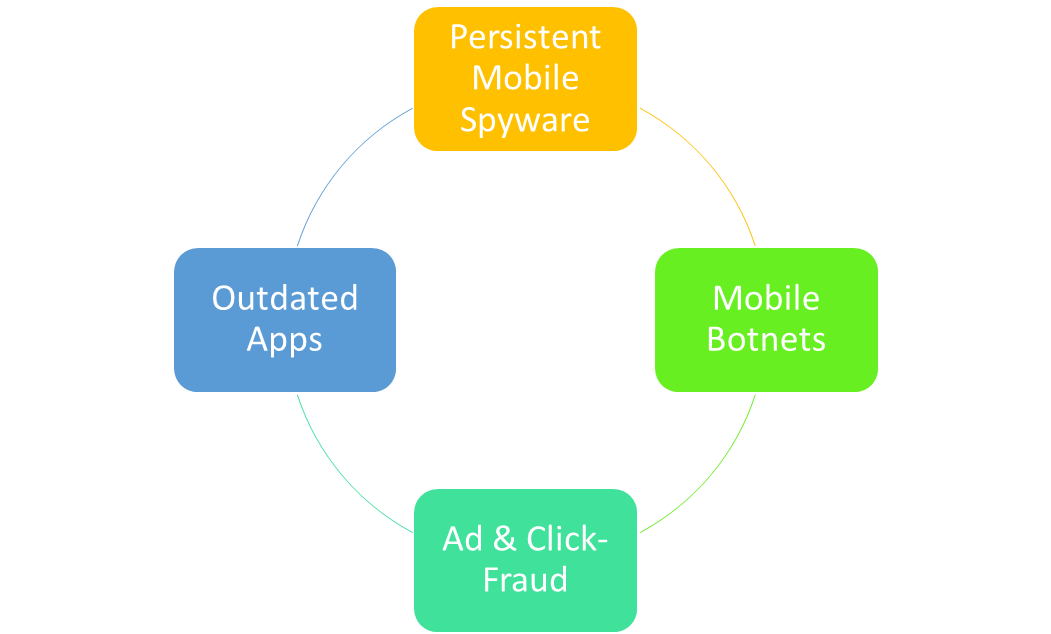
According to McAfee Labs, your mobile device is now a target for more than 1.5 million new incidents of mobile malware. Here are some quick tips for mobile device security:
- Create a Difficult Mobile Passcode – Not Your Birthdate or Bank PIN
- Install Apps from Trusted Sources
- Keep Your Device Updated – Hackers Use Vulnerabilities in Unpatched Older Operating Systems
- Avoid sending PII or sensitive information over text message or email
- Leverage Find my iPhone or the Android Device Manager to prevent loss or theft
- Perform regular mobile backups using iCloud or Enabling Backup & Sync from Android
Top New Threats in Mobile Security
8. Backup Your Data Regularly
Backing up your data regularly is an overlooked step in personal online security. The top IT and security managers follow a simple rule called the 3-2-1 backup rule. Essentially, you will keep three copies of your data on two different types of media (local and external hard drive) and one copy in an off-site location (cloud storage).
If you become a victim of ransomware or malware, the only way to restore your data is to erase your systems and restore with a recently performed backup.
9. Don’t Use Public Wi-Fi
Don’t use public Wi-Fi without using a Virtual Private Network (VPN). By using a VPN, the traffic between your device and the VPN server is encrypted. This means it’s much more difficult for a cybercriminal to obtain access to your data on your device. Use your cell network if you don’t have a VPN when security is important.
10. Review Your Online Accounts & Credit Reports Regularly for Changes
With the recent Equifax breach, it’s more important than ever for consumers to safeguard their online accounts and monitor their credit reports. A credit freeze is the most effective way for you to protect your personal credit information from cybercriminals right now. Essentially, it allows you to lock your credit and use a personal identification number (PIN) that only you will know. You can then use this PIN when you need to apply for credit.
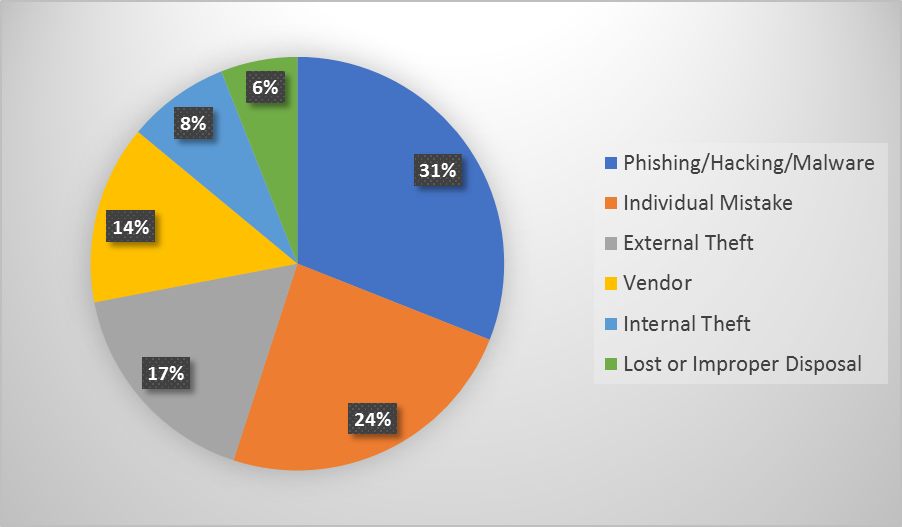
Top Causes of Security Breaches
Hacking, phishing, and malware incidents are becoming the number one cause of security breaches today. But, what’s more troubling, these hacking attempts are the result of human errors in some way. Education and awareness are critically important in the fight against cybercriminal activity and preventing security breaches.
We hope you found these personal cybersecurity tips and the knowledge of how personal security breaches occur to be helpful in mitigating your risk from a security incident.